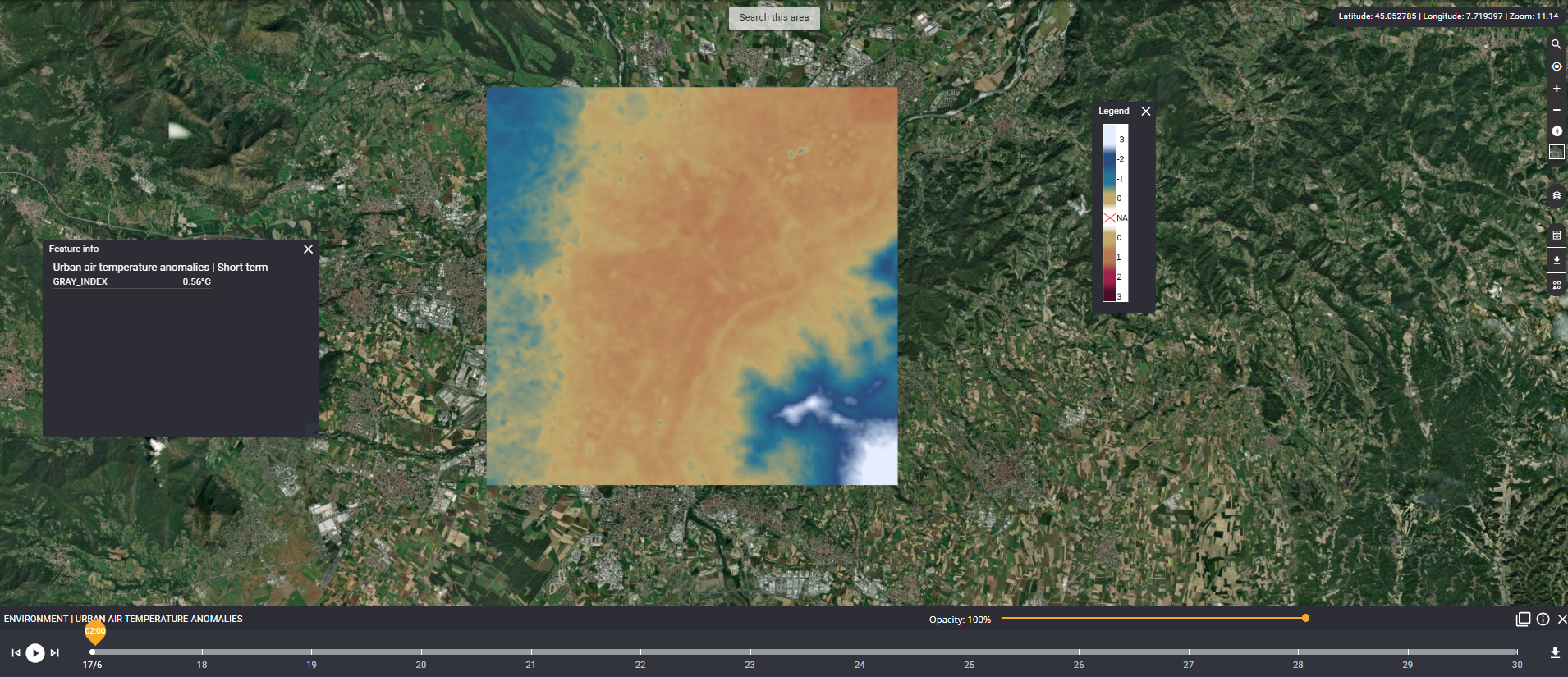

Unveiling Urban Heat Islands with AI: A Path to Cooler Cities
As cities grow larger and denser, the phenomenon of Urban Heat Islands (UHIs) becomes increasingly pronounced. UHIs are localized areas in cities where temperatures are significantly higher than surrounding rural regions. This temperature disparity, driven by urbanization and climate change, poses critical challenges for sustainability, public health, and infrastructure. However, a groundbreaking AI-based tool is changing the game by offering high-resolution temperature maps, enabling city planners to tackle UHIs with precision and foresight.
The Urban Heat Island Problem: A Global Concern
Urban Heat Islands emerge from a combination of human activities, reduced green spaces, and materials like concrete and asphalt that absorb and retain heat. During heatwaves, UHIs exacerbate health risks, strain energy grids, and disproportionately impact vulnerable populations. For example, studies reveal a 45% increase in heat-related mortality in areas heavily affected by UHIs. As global temperatures rise, addressing this issue becomes more urgent.
In Italy, cities like Turin frequently experience temperatures exceeding recommended limits. These soaring temperatures underscore the need for innovative solutions to mitigate the adverse effects of UHIs. Traditional approaches, such as planting trees or implementing green roofs, though effective, require targeted application informed by robust data. This is where the AI-based temperature mapping tool comes into play.
The AI Solution: High-Resolution Temperature Mapping
Developed through cutting-edge research, the new AI tool leverages machine learning techniques, particularly Visual Transformers, to generate detailed temperature maps. Using a mix of satellite data and meteorological predictions, the tool predicts maximum daily temperatures across urban landscapes at a resolution of 20 meters per pixel. This high level of detail allows for a granular understanding of temperature distribution within cities.
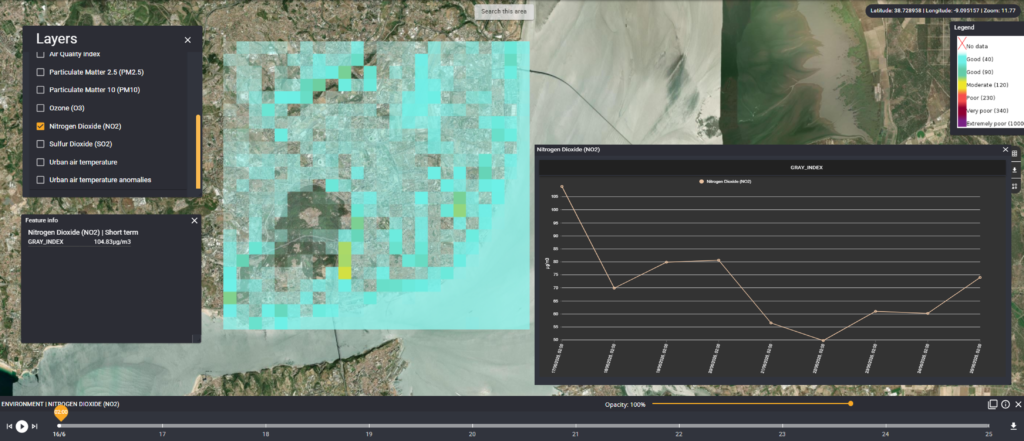
How It Works
The AI model combines data from the European Space Agency's Sentinel satellites, weather stations, and digital elevation models. By integrating these diverse data sources, the tool captures the complexity of urban microclimates. The model processes:
- Thermal data from satellites: Infrared bands measure land surface temperatures.
- Topographical features: The combination of Sentinel 1 and Sentinel 2 data gives information about the city morphology.
- Weather variables: Factors like humidity, wind speed, and air pressure.
Through sophisticated algorithms, the AI identifies temperature patterns and forecasts the hottest areas within a city. For example, industrial zones and densely built neighbourhoods often show elevated temperatures, while green spaces and water bodies provide cooling effects.
Real-World Application: Turin as a Testbed
The tool was tested in Turin, where it demonstrated remarkable accuracy, achieving a mean absolute error of just 1.3°C on downscaling and of 2.21°C on the 14 days forecast. The resulting temperature maps highlighted critical hotspots, such as densely populated urban centers, and cooler zones like parks and rivers.
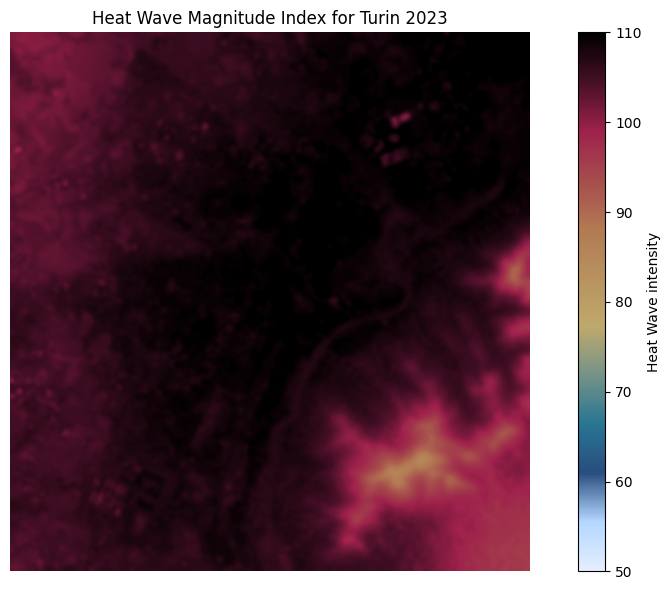
Beyond daily temperature forecasting, the tool enables a deeper analysis of urban heat stress through:
- Daily Downscaling: Generating high-resolution (20m) temperature maps for every day of the year, offering a continuous view of thermal conditions across the city.
- Heatwave Detection: Applying scientifically validated formulas (e.g., based on percentile thresholds or consecutive days above a temperature limit) to identify heatwave events throughout the year.
- Heatwave Intensity Calculation: For each detected heatwave day, the tool computes intensity using the downscaled temperature data, capturing the spatial variability of extreme heat.
- Annual Heatwave Burden Mapping: By summing the intensities of all heatwave days, the tool produces a cumulative heatwave exposure map.
This reveals which neighbourhoods are most frequently and severely affected by extreme heat and provides a powerful decision-support layer for urban resilience planning.
Informing Urban Regeneration with Nature-Based Solutions
Nature-based solutions (NBS) offer a sustainable and effective way to combat UHIs. These include planting urban forests, developing green roofs, and enhancing water features. However, implementing NBS without precise data can lead to inefficiencies or missed opportunities.
With high-resolution temperature maps, decision-makers can tailor NBS to specific urban contexts. For instance, in areas identified as UHI hotspots, planners can:
- Install reflective pavements to reduce heat absorption.
- Design parks that optimize cooling effects through strategic placement.
- Promote urban agriculture to enhance biodiversity and provide shade.
- Limit certain urban areas to private transportation.
Moreover, the tool supports equitable urban development by ensuring that disadvantaged communities, often the hardest hit by UHIs, are prioritized in mitigation efforts.
A Broader Perspective: Scaling Up the Solution
While Turin serves as a successful case study, the AI tool’s potential extends far beyond a single city. By adapting the model to different urban contexts, it can guide UHI mitigation efforts worldwide. Future enhancements, such as integrating population density and vegetation health indices, could further refine predictions and broaden their impact.
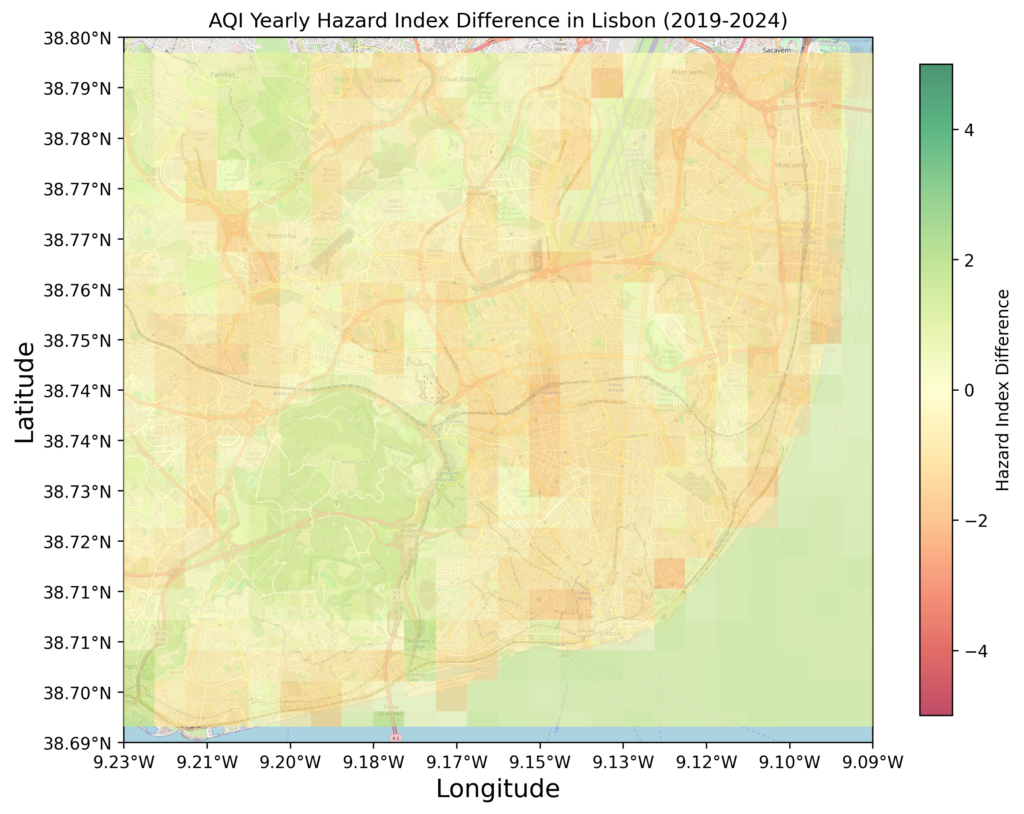
The Road Ahead
As cities continue to grow, the challenges posed by UHIs will only intensify. However, innovative technologies like this AI-based temperature mapping tool offer a beacon of hope. By combining scientific rigor with actionable insights, the tool equips urban planners, policymakers, and communities with the knowledge needed to create cooler, more sustainable cities.
In the face of a warming planet, addressing UHIs is not just a necessity but an opportunity to reimagine urban living. Through intelligent application of technology and nature-based solutions, we can build resilient cities that prioritize both environmental sustainability and human well-being.
Call to Action
It’s time for cities to embrace data-driven approaches to urban planning. By leveraging AI tools and investing in nature-based solutions, we can turn the tide against UHIs and create livable environments for future generations. Together, we can make our cities not only smarter but also cooler, in every sense of the word.


